

下一頁: 求
上一頁: Quadratic Reciprocity Law
前一頁: Quadratic Reciprocity Law
我們首先探討
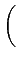
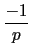
 的取值情形. 或許大家會疑惑當 a
是一個負整數時, 一定可以找到一正整數 b 使得
a
的取值情形. 或許大家會疑惑當 a
是一個負整數時, 一定可以找到一正整數 b 使得
a 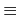 b(mod p),
因此利用 Lemma 5.3.2(2) 我們有
b(mod p),
因此利用 Lemma 5.3.2(2) 我們有


 =
= 

 ,
所以只要探討正整數的情況就好了為何還要考慮負的情況呢? 沒錯,
一般來說我們只要知道正整數的情形就足夠了,
不過考慮負整數也有其方便性. 例如我們要求
,
所以只要探討正整數的情況就好了為何還要考慮負的情況呢? 沒錯,
一般來說我們只要知道正整數的情形就足夠了,
不過考慮負整數也有其方便性. 例如我們要求


 . 因為
97
. 因為
97 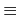 - 4 = (- 1)×22(mod 101), 利用 Lemma 5.3.2 以及
Proposition 5.3.5 馬上可得
- 4 = (- 1)×22(mod 101), 利用 Lemma 5.3.2 以及
Proposition 5.3.5 馬上可得


 =
= 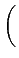

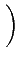 .
另一方面在 modulo p 之下是否有元素像複數中的 i 一樣滿足 i2 = - 1
原本也就是一個有趣的問題. 所以了解
.
另一方面在 modulo p 之下是否有元素像複數中的 i 一樣滿足 i2 = - 1
原本也就是一個有趣的問題. 所以了解
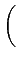
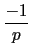
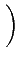 之值事實上是必要的.
之值事實上是必要的.
Euler's Criterion 雖然在算一般的


 不是很好用, 不過在算
不是很好用, 不過在算
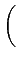
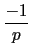
 就很好用了.
就很好用了.
証 明.
利用 Corollary
5.3.4 我們知
若
p 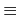
1(mod 4), 表示存在
k 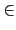
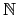
使得
p = 4
k + 1, 故得
(- 1)
(p - 1)/2 = (- 1)
2k = 1. 因此得證
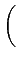
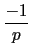
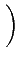
= 1. 若
p 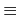
- 1(mod 4), 表示存在
k 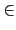
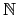
使得
p = 4
k - 1, 故得
(- 1)
(p - 1)/2 = (- 1)
2k - 1 = - 1. 因此得證
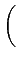
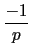
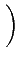
= - 1.
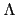
要注意由於 p 是奇質數, 因此 p 在 modulo 4 之下要不然和 1
同餘要不然就和 -1 同餘, 所以 Theorem 5.4.1 給了
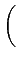
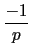
 完整的答案. 今後我們要知道
x2
完整的答案. 今後我們要知道
x2 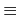 - 1(mod p) 是否有解時, 只要看
p 在 modulo 4 之情形就可以知道答案. 例如剛才我們想知道
x2
- 1(mod p) 是否有解時, 只要看
p 在 modulo 4 之情形就可以知道答案. 例如剛才我們想知道
x2 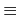 97(mod 101) 是否有解, 由
97(mod 101) 是否有解, 由


 =
= 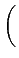

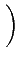 以及
101
以及
101 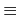 1(mod 4) 馬上知道
x2
1(mod 4) 馬上知道
x2 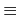 97(mod 101)
是有解的.
97(mod 101)
是有解的.
Li
2007-06-28
![]()
![]()
![]() 的取值情形. 或許大家會疑惑當 a
是一個負整數時, 一定可以找到一正整數 b 使得
a
的取值情形. 或許大家會疑惑當 a
是一個負整數時, 一定可以找到一正整數 b 使得
a ![]() b(mod p),
因此利用 Lemma 5.3.2(2) 我們有
b(mod p),
因此利用 Lemma 5.3.2(2) 我們有
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() ,
所以只要探討正整數的情況就好了為何還要考慮負的情況呢? 沒錯,
一般來說我們只要知道正整數的情形就足夠了,
不過考慮負整數也有其方便性. 例如我們要求
,
所以只要探討正整數的情況就好了為何還要考慮負的情況呢? 沒錯,
一般來說我們只要知道正整數的情形就足夠了,
不過考慮負整數也有其方便性. 例如我們要求
![]()
![]()
![]() . 因為
97
. 因為
97 ![]() - 4 = (- 1)×22(mod 101), 利用 Lemma 5.3.2 以及
Proposition 5.3.5 馬上可得
- 4 = (- 1)×22(mod 101), 利用 Lemma 5.3.2 以及
Proposition 5.3.5 馬上可得
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() .
另一方面在 modulo p 之下是否有元素像複數中的 i 一樣滿足 i2 = - 1
原本也就是一個有趣的問題. 所以了解
.
另一方面在 modulo p 之下是否有元素像複數中的 i 一樣滿足 i2 = - 1
原本也就是一個有趣的問題. 所以了解
![]()
![]()
![]() 之值事實上是必要的.
之值事實上是必要的.
![]()
![]()
![]() 不是很好用, 不過在算
不是很好用, 不過在算
![]()
![]()
![]() 就很好用了.
就很好用了.
