


下一頁: Galois 理論的例子
上一頁: Galois 理論的應用
前一頁: Primitive Element Theorem
目 錄
Trace 和 norm 是談論 finite extension
時兩個重要的函數.
Definition 4.2.3
假設
L/
K 是一個 finite separable extension 且
N 是
L/
K 的一個
normal closure. 令
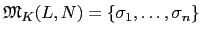
為所有
L 到
N 的
K-monomorphisms 所成的集合. 若
a  L
L, 我們定義
T
L/K(
a) =
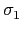
(
a) +
... +
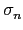
(
a) and N
L/K(
a) =
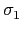
(
a)
... 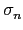
(
a).
T
L/K(
a) 和
N
L/K(
a) 分別稱作
a 的
trace 和
norm for
L/
K.
要注意 trace 和 norm 的取值與 extension 有關. 例如若 F 是 L/K 的
intermediate field 且 a  F, 則
TL/K(a) 和
TF/K(a)
可能不同; 同樣的
NL/K(a) 和
NF/K(a) 也可能不同.
接下來我們介紹一些 trace 和 norm 的基本性質.
F, 則
TL/K(a) 和
TF/K(a)
可能不同; 同樣的
NL/K(a) 和
NF/K(a) 也可能不同.
接下來我們介紹一些 trace 和 norm 的基本性質.
Lemma 4.2.4
假設
L/
K 是一個 finite separable extension 且 [
L :
K] =
n. 則對任意
a,
b  L
L 以及
k  K
K, 我們有以下的性質:
-
TL/K(ka + b) = kTL/K(a) + TL/K(b) 且
NL/K(ab) = NL/K(a)NL/K(b).
-
TL/K(k) = nk 且
NL/K(k) = kn.
証 明.
假設
N 是
L/
K 的一個 normal closure. 因為
L/
K 是 finite
separable extension, 由 Theorem
3.4.5 知
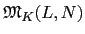
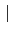
= [
L :
K] =
n. 現假設
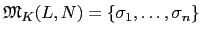
.
(1) 由於 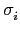 是 K-monomorphism, 我們有
是 K-monomorphism, 我們有
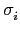 (ka + b) = k
(ka + b) = k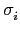 (a) +
(a) + 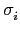 (b), 因此依定義得
(b), 因此依定義得
T
L/K(
ka +
b) =
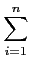
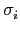
(
ka +
b) =
k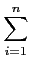
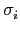
(
a) +
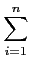
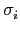
(
b) =
kT
L/K(
a) + T
L/K(
b).
同理, 因為
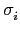
(
ab) =
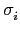
(
a)
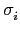
(
b), 故得
N
L/K(
ab) =
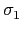
(
ab)
... 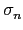
(
ab) = (
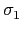
(
a)
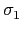
(
b))
... (
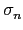
(
a)
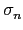
(
b)) =
NL/K(
a)
NL/K(
b).
(2) 由於
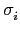 (k) = k, 故直接依定義知
(k) = k, 故直接依定義知
TL/K(
k) =
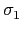
(
k) +
... +
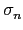
(
k) =
nk and N
L/K(
k) =
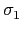
(
k)
... 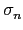
(
k) =
kn.
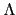
當 L/K 是 Galois extension 時, 因為 L/K 是 normal extension,
故由 Lemma 3.2.6 得
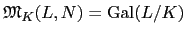 , 因此若
Gal(L/K) = {
, 因此若
Gal(L/K) = {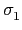 ,...,
,...,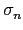 }, 則對任意
}, 則對任意
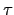
 Gal(L/K),
由於
Gal(L/K) 是一個 group, 我們有
Gal(L/K) = {
Gal(L/K),
由於
Gal(L/K) 是一個 group, 我們有
Gal(L/K) = {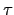 o
o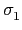 ,...,
,...,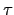 o
o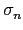 }.
因此依定義知
}.
因此依定義知
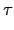
(T
L/K(
a)) =
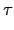
(
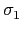
(
a) +
... 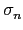
(
a)) =
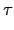
(
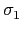
(
a)) +
... +
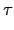
(
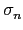
(
a)) = T
L/K(
a).
同理知
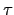 (NL/K(a)) = NL/K(a). 也就是說
TL/K(a) 和
NL/K(a) 皆落在
Gal(L/K) 的 fixed field 中. 但由於假設 L/K
是 Galois extension, 故由 Theorem 4.1.1 知
Gal(L/K) 的
fixed field 為 K, 得證
TL/K(a)
(NL/K(a)) = NL/K(a). 也就是說
TL/K(a) 和
NL/K(a) 皆落在
Gal(L/K) 的 fixed field 中. 但由於假設 L/K
是 Galois extension, 故由 Theorem 4.1.1 知
Gal(L/K) 的
fixed field 為 K, 得證
TL/K(a)  K 且
NL/K(a)
K 且
NL/K(a)  K.
當 L/K 僅是 finite separable extension 時, 我們依然可利用 Galois
理論證得
TL/K(a)
K.
當 L/K 僅是 finite separable extension 時, 我們依然可利用 Galois
理論證得
TL/K(a)  K 且
NL/K(a)
K 且
NL/K(a)  K.
K.
Proposition 4.2.5
假設
L/
K 是 finite separable extension. 則對任意
a  L
L, 皆有
T
L/K(
a)
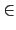 K
K and N
L/K(
a)
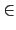 K
K.
証 明.
若
N 是
L/
K 的一個 normal closure, 則由 Lemma
4.2.1 知
N/
K 是 finite Galois extension. 假設
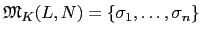
. 對任意
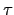

Gal(
N/
K),
由於
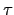 o
o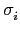
:
L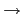 N
N 是
K-monomorphism, 我們知
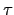
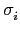

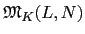
. 又若
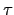 o
o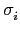
=
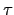 o
o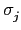
, 則因
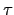
是 1-1 可得
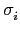
=
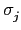
. 因此我們知對任意
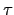

Gal(
N/
K) 皆有
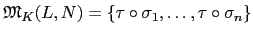
.
所以依定義知對任意
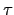

Gal(
N,
K) 皆有
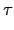
(T
L/K(
a)) =
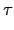
(
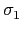
(
a) +
... 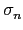
(
a)) =
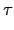
(
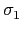
(
a)) +
... +
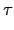
(
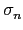
(
a)) = T
L/K(
a).
同理知
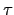
(N
L/K(
a)) = N
L/K(
a). 也就是說
T
L/K(
a) 和
N
L/K(
a) 皆落在
Gal(
N/
K) 的 fixed field 中. 故由
N/
K 是
Galois extension 以及 Theorem
4.1.1 知
T
L/K(
a)
 K
K
且
N
L/K(
a)
 K
K.
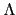
若 L/K 是 finite separable extension 且 F 是 L/K 的
intermediate field, 則 L/F 和 F/K 皆為 finite separable
extension (Lemma 3.4.2), 所以我們有 L/F 和 F/K 的 trace
和 norm. 現若 a  L, 則由 Proposition 4.2.5 知
TL/F(a) 和
NL/F(a) 皆為 F 中的元素, 所以可以將它們代入
TF/K 以及
NF/K 中, 得
TF/K(TL/F(a)) 以及
NF/K(NL/F(a)). 事實上它們會分別等於
TL/K(a) 以及
NL/K(a), 這就是 trace 和 norm 的 transitive property.
L, 則由 Proposition 4.2.5 知
TL/F(a) 和
NL/F(a) 皆為 F 中的元素, 所以可以將它們代入
TF/K 以及
NF/K 中, 得
TF/K(TL/F(a)) 以及
NF/K(NL/F(a)). 事實上它們會分別等於
TL/K(a) 以及
NL/K(a), 這就是 trace 和 norm 的 transitive property.
Proposition 4.2.6
假設
L/
K 是 finite separable extension 且
F 是
L/
K 的
intermediate field. 則對任意
a  L
L, 皆有
TF/K(TL/F(a)) = TL/K(a) and NF/K(NL/F(a)) = NL/K(a).
証 明.
若
N 是
L/
K 的一個 normal closure, 則由於
N/
K 是 normal
extension 且
F 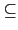 L
L 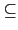 N
N, 利用 normal closure
的定義知存在
N' 是
F/
K 的 normal closure 且
N' 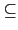 N
N.
假設
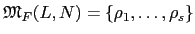 且
且
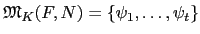 , 由於 N/K 是一個 finite
normal extension 且 F 是 N/K 的一個 intermediate field, 利用
Theorem 3.2.7 知每一個 K-monomorphism
, 由於 N/K 是一個 finite
normal extension 且 F 是 N/K 的一個 intermediate field, 利用
Theorem 3.2.7 知每一個 K-monomorphism
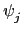 : F
: F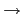 N
都可以 extends 成一個 K-monomorphism
N
都可以 extends 成一個 K-monomorphism
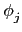 : N
: N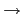 N (即
N (即
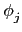 |F =
|F = 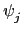 ). 在 Lemma 3.2.12 的證明中我們證得
). 在 Lemma 3.2.12 的證明中我們證得
因此知
T
L/K(
a) =
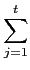
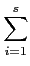
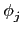
(
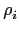
(
a)) =
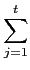
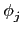
(
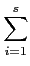
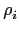
(
a)) =
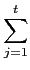
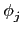
(T
L/F(
a)).
另一方面利用 Corollary
3.2.11 我們知
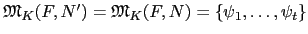
以及利用
Proposition
4.2.5 我們知
T
L/F(
a)
 F
F, 因此
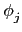
(T
L/F(
a)) =
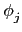
|
F(T
L/F(
a)) =
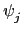
(T
L/F(
a)).
故得
T
F/K(T
L/F(
a)) =
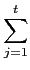
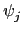
(T
L/F(
a)) =
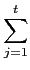
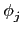
(T
L/F(
a)) = T
L/K(
a).
同理證得
N
F/K(N
L/F(
a)) =
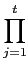
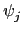
(N
L/F(
a)) =
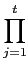
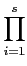
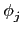
(
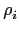
(
a)) = N
L/K(
a).
因為一個 finite extension 的 normal closure 並不唯一, 由定義 trace
和 norm 的取值可能會和 normal closure 的選取有關.
我們最後就是要探討這個問題, 事實上我們得到一個元素的 trace 與 norm
和它的 minimal polynomial 有關, 也因此得知 trace 和 norm 和 normal
closure 的選取無關.
Theorem 4.2.7
假設
L/
K 是 finite separable extension 且 [
L :
K] =
n. 若
a  L
L 且
a over
K 的 minimal polynomial 為
f (
x) =
xm +
am - 1xm - 1 +
... +
a1x +
a0, 則
T
L/K(
a) = -
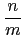 am - 1
am - 1 and N
L/K(
a) = (- 1)
na0n/m.
証 明.
令
F =
K(
a), 由於
f (
x) 是
a over
K 的 minimal polynomial 且
deg(
f (
x)) =
m, 知 [
F :
K] =
m, 故得
[
L :
F] = [
L :
K]/[
F :
K] =
n/
m. 因此由
a  F
F 以及 Lemma
4.2.4 (2) 知
T
L/F(
a) = (
n/
m)
a 以及
N
L/F(
a) =
an/m. 接著我們要計算
T
F/K(
a) 以及
N
F/K(
a).
令 N 為 F/K 的一個 normal closure, 因為 L/K 是 finite
separable extension, 故知 F/K 也是 finite separable extension
(Lemma 3.4.2), 因此由 Theorem 3.4.5 知
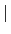
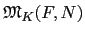
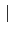 = [F : K] = m. 假設
= [F : K] = m. 假設
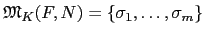 . 由於 F = K(a) 是一個 over
K 的 simple extension, 每一個 F 到 N 的 K-monomorphism 都由
a 的取值唯一確定. 所以得
. 由於 F = K(a) 是一個 over
K 的 simple extension, 每一個 F 到 N 的 K-monomorphism 都由
a 的取值唯一確定. 所以得
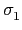 (a),...,
(a),...,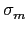 (a) 皆相異.
又因為
(a) 皆相異.
又因為
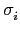 (a) 必為 f (x) 的根, 所以得
(a) 必為 f (x) 的根, 所以得
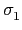 (a),...,
(a),...,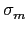 (a) 剛好就是 f (x) 所有的根. 故得
f (x) = (x -
(a) 剛好就是 f (x) 所有的根. 故得
f (x) = (x - 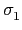 (a)) ... (x -
(a)) ... (x - 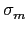 (a)). 利用根與係數的關係,
我們得到
(a)). 利用根與係數的關係,
我們得到
T
F/K(
a) =
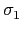
(
a) +
... +
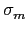
(
a) = -
am - 1
以及
N
F/K(
a) =
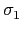
(
a)
... 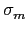
(
a) = (- 1)
ma0.
因此利用
Proposition
4.2.6 以及 Lemma
4.2.4 (1) 得證
T
L/K(
a) = T
F/K(
TL/F(
a)) = T
F/K(
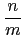 a
a) =
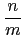 TF/K
TF/K(
a) = -
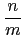 am - 1
am - 1
以及
NL/K(a) = NF/K(NL/F(a)) = NF/K(an/m) = NF/K(a)n/m = ((- 1)ma0)n/m = (- 1)na0n/m.
由 Theorem 4.2.7 可以看出, 不僅
TL/K(a)  K 且
NL/K(a)
K 且
NL/K(a)  K 而且 trace 和 norm 的取值和 L/K 的 normal
closure 的選取無關.
K 而且 trace 和 norm 的取值和 L/K 的 normal
closure 的選取無關.



下一頁: Galois 理論的例子
上一頁: Galois 理論的應用
前一頁: Primitive Element Theorem
目 錄
Li
2006-05-18
![]() 是 K-monomorphism, 我們有
是 K-monomorphism, 我們有
![]() (ka + b) = k
(ka + b) = k![]() (a) +
(a) + ![]() (b), 因此依定義得
(b), 因此依定義得
![]() (k) = k, 故直接依定義知
(k) = k, 故直接依定義知
![]() , 因此若
Gal(L/K) = {
, 因此若
Gal(L/K) = {![]() ,...,
,...,![]() }, 則對任意
}, 則對任意
![]()
![]() Gal(L/K),
由於
Gal(L/K) 是一個 group, 我們有
Gal(L/K) = {
Gal(L/K),
由於
Gal(L/K) 是一個 group, 我們有
Gal(L/K) = {![]() o
o![]() ,...,
,...,![]() o
o![]() }.
因此依定義知
}.
因此依定義知
![]() L, 則由 Proposition 4.2.5 知
TL/F(a) 和
NL/F(a) 皆為 F 中的元素, 所以可以將它們代入
TF/K 以及
NF/K 中, 得
TF/K(TL/F(a)) 以及
NF/K(NL/F(a)). 事實上它們會分別等於
TL/K(a) 以及
NL/K(a), 這就是 trace 和 norm 的 transitive property.
L, 則由 Proposition 4.2.5 知
TL/F(a) 和
NL/F(a) 皆為 F 中的元素, 所以可以將它們代入
TF/K 以及
NF/K 中, 得
TF/K(TL/F(a)) 以及
NF/K(NL/F(a)). 事實上它們會分別等於
TL/K(a) 以及
NL/K(a), 這就是 trace 和 norm 的 transitive property.
![]() 且
且
![]() , 由於 N/K 是一個 finite
normal extension 且 F 是 N/K 的一個 intermediate field, 利用
Theorem 3.2.7 知每一個 K-monomorphism
, 由於 N/K 是一個 finite
normal extension 且 F 是 N/K 的一個 intermediate field, 利用
Theorem 3.2.7 知每一個 K-monomorphism
![]() : F
: F![]() N
都可以 extends 成一個 K-monomorphism
N
都可以 extends 成一個 K-monomorphism
![]() : N
: N![]() N (即
N (即
![]() |F =
|F = ![]() ). 在 Lemma 3.2.12 的證明中我們證得
). 在 Lemma 3.2.12 的證明中我們證得
![]()
![]()
![]() = [F : K] = m. 假設
= [F : K] = m. 假設
![]() . 由於 F = K(a) 是一個 over
K 的 simple extension, 每一個 F 到 N 的 K-monomorphism 都由
a 的取值唯一確定. 所以得
. 由於 F = K(a) 是一個 over
K 的 simple extension, 每一個 F 到 N 的 K-monomorphism 都由
a 的取值唯一確定. 所以得
![]() (a),...,
(a),...,![]() (a) 皆相異.
又因為
(a) 皆相異.
又因為
![]() (a) 必為 f (x) 的根, 所以得
(a) 必為 f (x) 的根, 所以得
![]() (a),...,
(a),...,![]() (a) 剛好就是 f (x) 所有的根. 故得
f (x) = (x -
(a) 剛好就是 f (x) 所有的根. 故得
f (x) = (x - ![]() (a)) ... (x -
(a)) ... (x - ![]() (a)). 利用根與係數的關係,
我們得到
(a)). 利用根與係數的關係,
我們得到